Tech Article


Published on:
DFOG, short for Digital FOG or Digital Fiber Optic Gyroscope, is patent pending technology which has been developed over 25 years involving two research institutions. DFOG was created to meet the demand for smaller and more cost effective FOGs, while increasing reliability and accuracy.
This technological breakthrough enables new opportunities for commercial and defense applications requiring always available, ultra-high accuracy, orientation and navigation.
Fiber optic gyroscopes have set a high standard for inertial navigation. Their performance and accuracy have been recognized for several decades, with each generation offering innovative improvements.
The first generation of FOG made available in 1976 used analog signals and analog signal processing. The second generation was developed in 1994 and is still used to this day. It improved upon the first generation with a hybrid approach using an analog signal in the coil with digital signal processing.
In 2021, FOG has evolved into Digital FOG. This third generation of FOG sets itself apart by being completely digital, providing higher performance and reliability while enabling a 40% reduction in size, weight, power and cost (SWaP-C).
The innovations that make DFOG possible are three different, yet complimentary, technologies that have been developed to improve the capabilities of fiber optic gyroscopes.
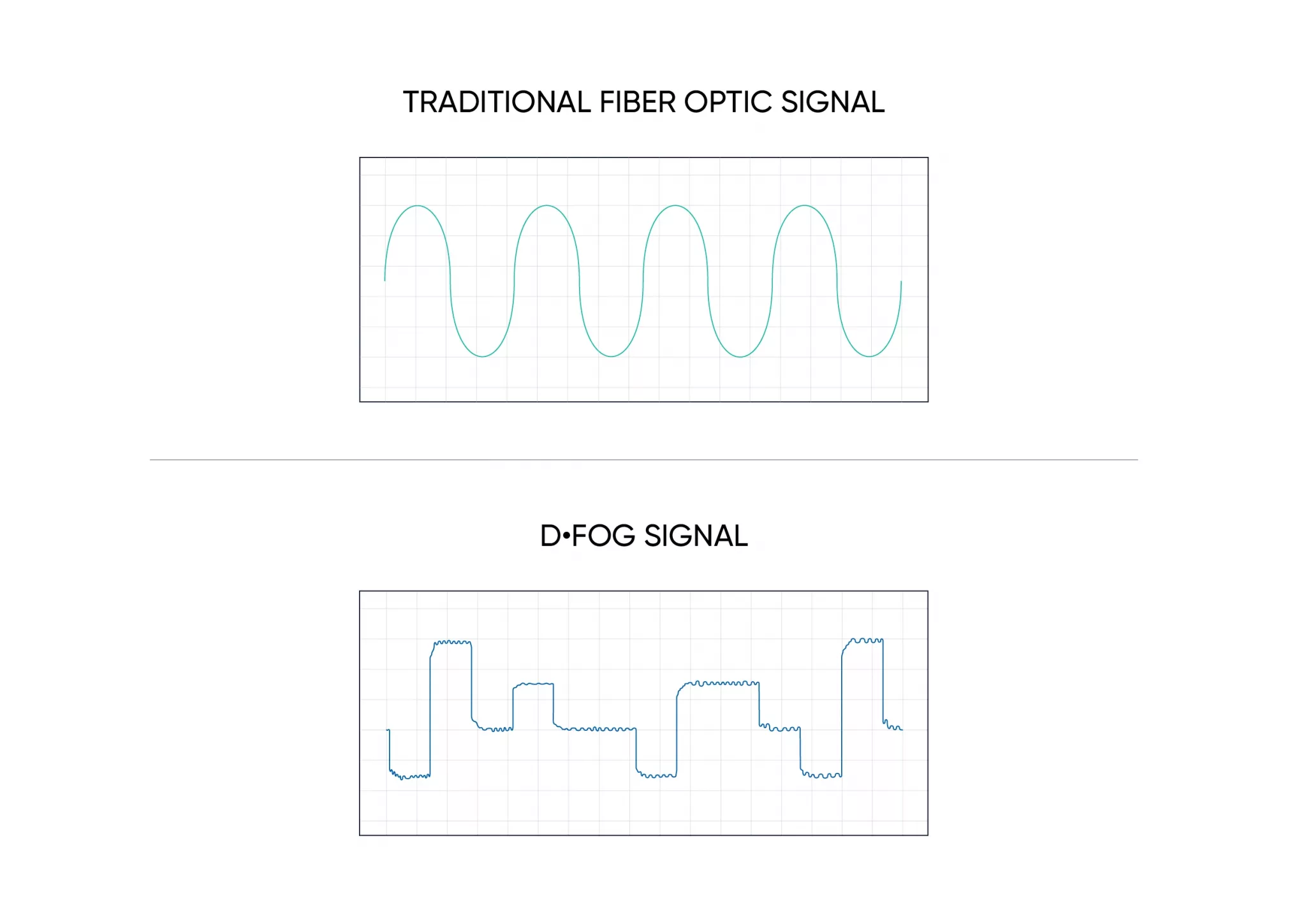
DFOG uses a specially developed digital modulation technique passing spread spectrum signals through the coil. The new digital modulation technique introduced in DFOG technology allows in-run variable errors in the coil to be measured and removed from the measurements. This makes DFOG significantly more stable and reliable than traditional FOGs. It also allows a smaller FOG with less coil length to achieve the accuracy of one with a longer coil.
By integrating 5 sensitive components into a single chip and removing all the fibre splices, the size, weight and power is reduced considerably while significantly improving reliability and performance.
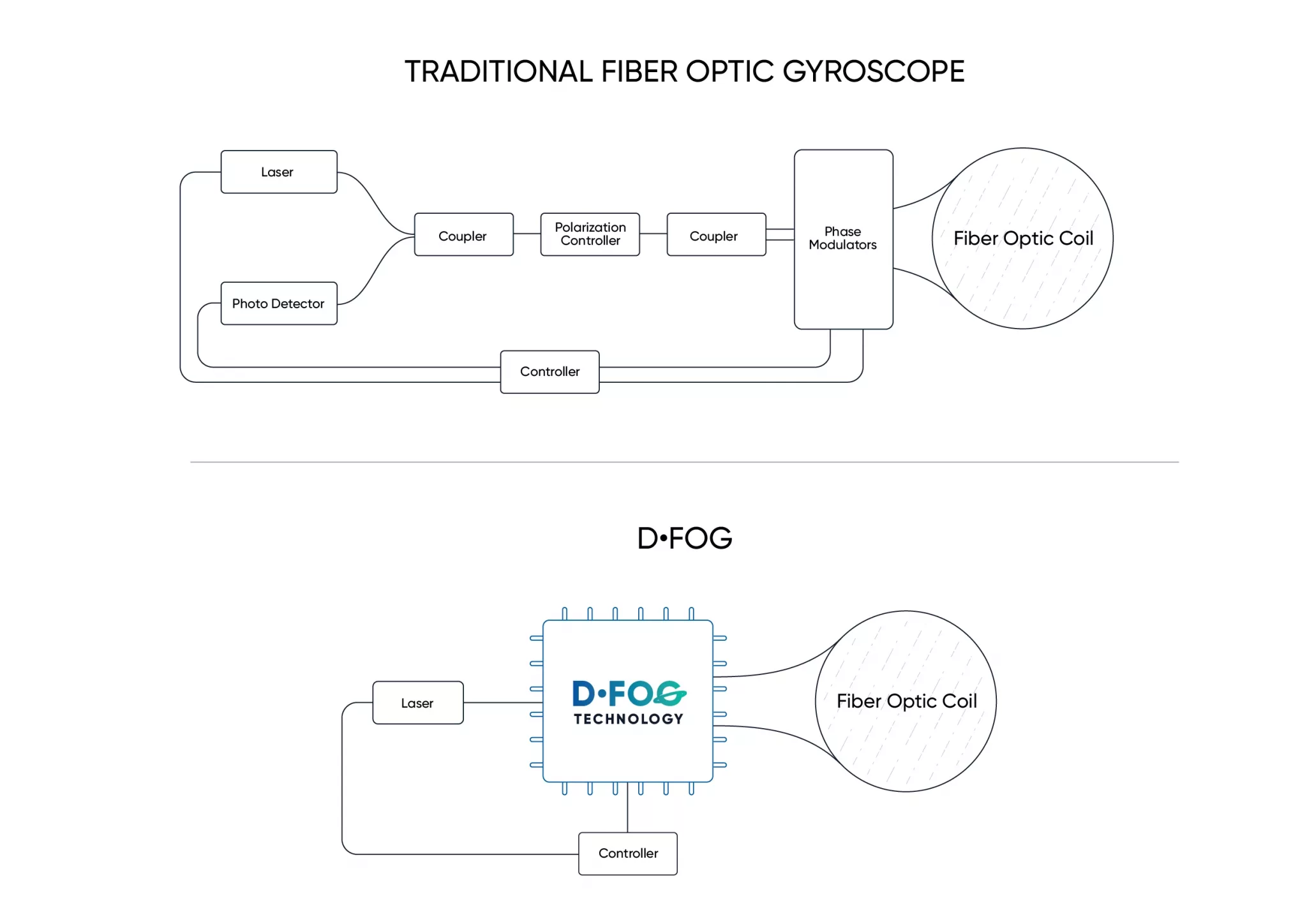
DFOG employs a specially designed closed-loop optical coil, developed to take full advantage of the digital modulation techniques. The design allows for optimum sensing of in-run variable coil errors using the new digital modulation technique. It also provides a very high level of protection for the optical components from shock and vibration.
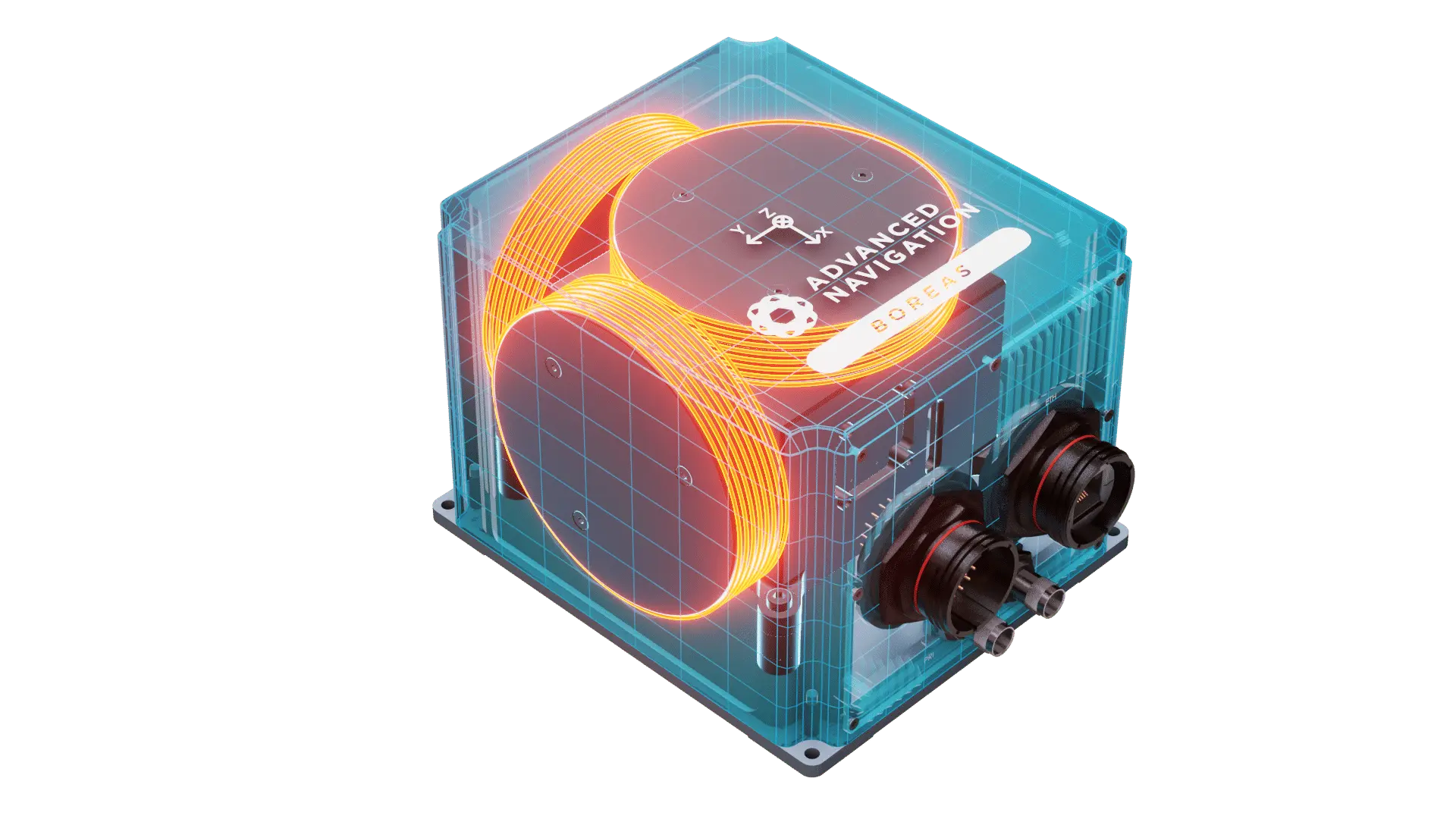

During the last two decades, FOGs have been the gyroscope of choice for high-performance Inertial Navigation Systems (INS). But their prohibitive cost and large size made them unsuitable for many applications. DFOG mitigates these limitations, while significantly improving accuracy and reliability.
DFOG makes high accuracy inertial navigation affordable and suitable for a larger number of applications, including subsea, surveying, marine, robotics, aerospace and space.

20 May 2025
Go to Article
30 March 2025
Go to Article